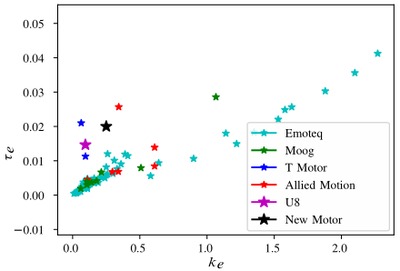
This paper proposes a new multi-input brushless DC motor current control policy aimed at robotics applications. The controller achieves empirical improvements in steady-state torque and power-production abilities relative to conventional controllers, while retaining similarly good torque-tracking and stability characteristics. Simulations show that non-conventional motor design optimizations whose feasibility is established by scaling model extrapolations from existing motor catalogues can vastly amplify the effectiveness of this new control-strategy.