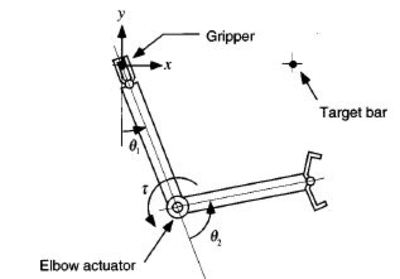
We report on our empirical studies of a new controller for a two-link brachiating robot. Motivated by the pendulum-like motion of an ape’s brachiation, we encode this task as the output of a “target dynamical system.” Numerical simulations indicate that the resulting controller solves a number of brachiation problems that we term the “ladder,” “swing-up,” and “rope” problems. Preliminary analysis provides some explanation for this success. The proposed controller is implemented on a physical system in our laboratory. The robot achieves behaviors including “swing locomotion” and “swing up” and is capable of continuous locomotion over several rungs of a ladder. We discuss a number of formal questions whose answers will be required to gain a full understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of this approach.